Of course it’s better to study in China. China boasts world-renowned universities, abundant academic resources and research opportunities, as well as low tuition and living costs. China’s rapid development has made it one of the world’s largest economies, offering vast opportunities for jobs and internships. In addition, China’s cultural diversity, long history and rich traditional arts provide students with a unique cultural experience. Therefore, choosing to study in China will provide students with comprehensive educational and professional development opportunities.
Table of Contents
The decision to study abroad is an exciting and life-changing experience. When considering studying in China or Japan, it is crucial to understand the educational systems, academic programs, teaching methods, research opportunities, language considerations, and various other factors. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison between studying in China and Japan, helping prospective students make an informed decision.
Educational System in China
Overview of Chinese Universities
Chinese universities have gained international recognition for their academic excellence and research contributions. The country boasts a vast network of universities, including prestigious institutions like Peking University, Tsinghua University, and Fudan University. These universities offer a wide range of programs and attract students from all over the world.
Academic Programs and Majors
Chinese universities provide diverse academic programs and majors across various fields, including engineering, medicine, business, arts, and social sciences. Students can pursue undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral degrees, tailoring their education to their interests and career goals. The universities often collaborate with industries and businesses to ensure the relevance and practicality of their programs.

Teaching Methods and Learning Environment
Chinese universities emphasize a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Lectures, seminars, laboratory work, and group projects are common teaching methods. The learning environment fosters critical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and teamwork. Many universities in China have modern facilities and state-of-the-art technologies to enhance the learning experience.
Research Opportunities
China has made significant investments in research and development, making it an attractive destination for students interested in research opportunities. Many universities have well-established research centers and partnerships with industries. These collaborations create ample opportunities for students to engage in cutting-edge research projects and contribute to advancements in their fields.
Language Considerations
Chinese is the primary language of instruction in most Chinese universities. While proficiency in Mandarin is beneficial for international students, some universities offer programs taught in English, particularly at the postgraduate level. However, learning the Chinese language can enhance cultural immersion, communication with locals, and open doors to broader career prospects.
Panda Brand
Panda, a well-known Chinese brand, represents various products, including electronics, food, and beverages. The brand is recognized for its quality and innovation in the market.
Please note that the information provided is for illustrative purposes only and may not reflect the actual content.
Educational System in Japan
Overview of Japanese Universities
Japanese universities are renowned for their academic excellence, cutting-edge research, and strong industry connections. Institutions like the University of Tokyo, Kyoto University, and Osaka University are among the top-ranked universities globally. Japanese universities offer a wide range of academic programs and provide a unique cultural experience for international students.
Academic Programs and Majors
Japanese universities offer a diverse range of academic programs and majors in fields such as engineering, medicine, humanities, social sciences, and more. Students can choose from undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral degrees, allowing them to specialize in their areas of interest. The curriculum focuses on a holistic education, combining theoretical knowledge with practical applications.
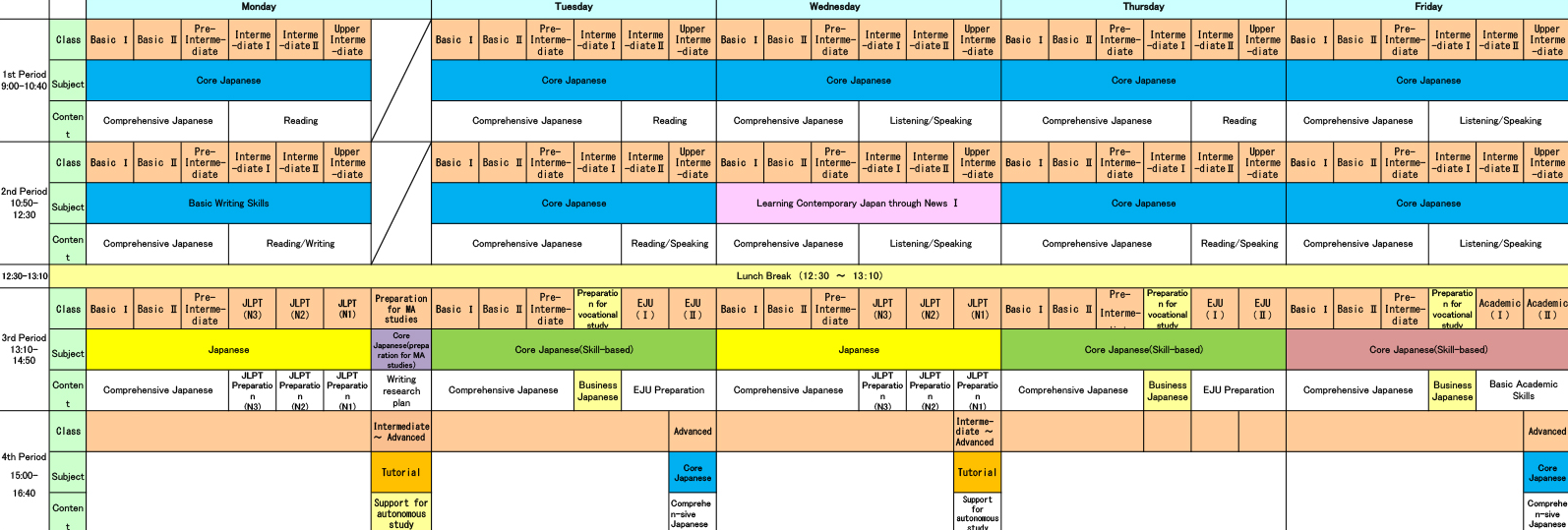
Teaching Methods and Learning Environment
Japanese universities employ a combination of traditional and modern teaching methods. Lectures, seminars, group discussions, and hands-on practical exercises are common in the Japanese education system. The learning environment promotes active participation, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. Students also benefit from well-equipped laboratories, libraries, and research centers.
Research Opportunities
Japan has a strong emphasis on research and innovation, making it an attractive destination for aspiring researchers. Japanese universities are at the forefront of various scientific, technological, and interdisciplinary research areas. Collaborations with industries, government agencies, and international institutions provide students with extensive research opportunities and access to state-of-the-art facilities.
Language Considerations
The primary language of instruction in Japanese universities is Japanese. However, an increasing number of universities are offering programs taught in English to attract international students. Proficiency in the Japanese language can greatly enhance the study experience, cultural immersion, and opportunities for part-time jobs or internships. Learning Japanese can also deepen understanding of Japanese culture and facilitate interactions with local communities.
Cost of Education
Tuition Fees
Tuition fees vary between China and Japan and can depend on factors such as the university, program of study, and degree level. Here is a comparison of average tuition fees for international students:
| Country | Undergraduate | Postgraduate |
|---|---|---|
| China | $3,000 – $10,000/year | $4,000 – $15,000/year |
| Japan | $6,000 – $15,000/year | $7,000 – $20,000/year |
It is important to note that these figures are approximate and can vary significantly depending on the specific university and program.
Scholarships and Financial Aid
Both China and Japan offer scholarships and financial aid opportunities for international students to help alleviate the cost of education. Some popular scholarships include:
- China:
- Chinese Government Scholarship (CSC)
- Confucius Institute Scholarship
- Provincial and university-specific scholarships
- Japan:
- Japanese Government (MEXT) Scholarships
- JASSO Scholarships
- University-specific scholarships
These scholarships provide financial support for tuition fees, living expenses, and sometimes include additional benefits such as accommodation and travel allowances. Eligibility criteria and application processes vary, so it is essential to research and apply for scholarships well in advance.
Living Expenses
When considering the cost of studying abroad, it is crucial to factor in living expenses. Here is an estimate of average monthly living expenses for international students:
| Country | Accommodation | Meals | Transportation | Other Expenses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | $300 – $800 | $150 – $300 | $20 – $60 | $100 – $200 |
| Japan | $500 – $1,000 | $200 – $400 | $40 – $100 | $150 – $300 |
Living expenses can vary based on the city, lifestyle choices, and personal preferences. It is important to consider these costs and plan accordingly.
Quality of Education
Academic Reputation
Both China and Japan have universities with strong academic reputations. Some institutions are globally recognized for their excellence in specific fields. For example:
- China:
- Tsinghua University, known for its engineering and technology programs.
- Peking University, renowned for its humanities and social sciences programs.
- Fudan University, recognized for its business and economics programs.
- Japan:
- The University of Tokyo, highly regarded for its science and technology programs.
- Kyoto University, known for its research in natural sciences and humanities.
- Osaka University, recognized for its medicine and life sciences programs.
International Rankings
International rankings provide insights into the overall standing of universities worldwide. Some prominent rankings include:
- China:
- Tsinghua University and Peking University are consistently ranked among the top universities in Asia according to QS World University Rankings and Times Higher Education World University Rankings.
- Japan:
- The University of Tokyo and Kyoto University consistently rank among the top universities globally according to QS World University Rankings and Times Higher Education World University Rankings.
Faculty and Research Output
The quality of faculty and research output is an important consideration when evaluating the quality of education. Both China and Japan have highly qualified faculty members and contribute to cutting-edge research in various fields. Many professors and researchers in these countries have made significant contributions to their respective disciplines.
Employability and Career Prospects
When considering studying in China or Japan, it is important to evaluate the employability and career prospects available in each country.
Cultural Experience and Language Learning
Cultural Diversity and Experiences in China
China is a culturally diverse country with a rich history spanning thousands of years. Here are some key aspects of cultural diversity and experiences in China:
Historical and Architectural Marvels
China is home to iconic landmarks such as the Great Wall, the Forbidden City, and the Terracotta Warriors. These historical sites offer a glimpse into China’s ancient civilization and architectural wonders.
Ethnic Diversity
China has 56 officially recognized ethnic groups, each with its own traditions, languages, and cultural practices. From the vibrant festivals of the Han majority to the unique customs of minority groups like the Tibetan, Uyghur, and Zhuang, students have the opportunity to immerse themselves in diverse cultural experiences.
Cuisine
Chinese cuisine is renowned worldwide for its variety and flavors. From spicy Sichuan dishes to delicate Cantonese dim sum, students can explore a wide range of regional delicacies. Sampling local street food and experiencing traditional tea ceremonies are also popular cultural experiences.
Learn more about Chinese culture on Wikipedia.
Cultural Diversity and Experiences in Japan
Japan has a unique cultural identity that blends traditional customs with modern influences. Here are some highlights of cultural diversity and experiences in Japan:
Traditional Arts and Performances
Japan is known for its traditional arts, including tea ceremonies, calligraphy, kimono dressing, and ikebana (flower arrangement). Students can participate in these activities and gain a deeper understanding of Japanese aesthetics and cultural practices.
Festivals
Japan hosts numerous vibrant festivals throughout the year, such as the Cherry Blossom Festival (Hanami), Gion Matsuri in Kyoto, and the Sapporo Snow Festival. These festivals showcase traditional dances, music, food, and fireworks, providing students with an immersive cultural experience.
Pop Culture
Japan’s pop culture, including anime, manga, and J-pop, has gained global popularity. Students can explore anime and manga museums, attend cosplay events, and visit vibrant neighborhoods like Akihabara in Tokyo to experience the unique blend of traditional and modern Japanese pop culture.
Learn more about Japanese culture on Wikipedia.
Language Learning Opportunities
Studying in China or Japan provides excellent opportunities for language learning:
Chinese Language Learning Opportunities
Studying in China allows students to immerse themselves in Mandarin, the most widely spoken language in the country. Universities often provide Chinese language courses for international students, enabling them to enhance their language skills. Interacting with local students and practicing conversational Mandarin in daily life further accelerates language learning.

Japanese Language Learning Opportunities
Japan offers an immersive environment for learning Japanese. Many universities provide Japanese language programs for international students at various proficiency levels. Engaging with local communities, participating in language exchange programs, and practicing conversational Japanese in daily interactions contribute to language proficiency development.
Personal Growth and Global Perspective
Studying in China or Japan offers students the opportunity for personal growth and a broader global perspective:
Cultural Sensitivity and Adaptability
Living in a foreign country fosters cultural sensitivity, adaptability, and the ability to navigate diverse environments. Students develop cross-cultural communication skills and gain a deeper appreciation for different perspectives.
Expanded Worldview
Interacting with students from different countries and backgrounds broadens students’ worldview and encourages a global mindset. Exposure to different educational systems, ideologies, and experiences enhances critical thinking and promotes a deeper understanding of global issues.
Networking and International Connections
Studying abroad allows students to build a diverse network of friends, classmates, and mentors from around the world.
Visa Requirements and Ease of Integration
Visa Process in China
To study in China, international students typically need to apply for a student visa (X visa). Here are some key points regarding the visa process:
Application Procedure
Students must first secure admission to a Chinese university and receive an acceptance letter. With the necessary documents, including the admission letter and a valid passport, students can apply for a student visa at the Chinese embassy or consulate in their home country.
Requirements
The specific requirements for a student visa may vary depending on the country of origin and the Chinese embassy or consulate. Generally, students are required to submit a completed visa application form, passport-sized photos, proof of financial resources, and a valid health certificate.
Residence Permit
After arrival in China, students must obtain a residence permit within 30 days. The university’s international student office assists with the application process, which involves providing additional documents and completing a health check.
Learn more about the Chinese visa process on Wikipedia.
Visa Process in Japan
International students planning to study in Japan usually need a student visa. Here are some key points about the visa process:
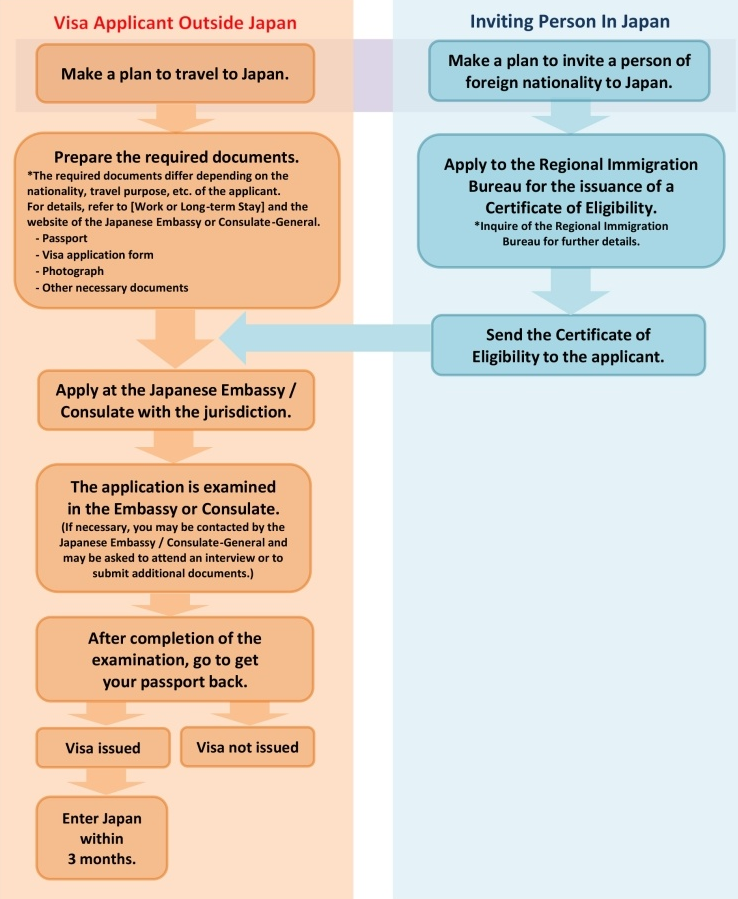
Certificate of Eligibility
Before applying for a student visa, students must obtain a Certificate of Eligibility (COE) from their chosen Japanese university or a sponsoring organization. The COE serves as a prerequisite for the student visa application.
Visa Application
With the COE and other required documents, students can apply for a student visa at the Japanese embassy or consulate in their home country. The application usually includes a completed visa application form, passport-sized photos, a valid passport, the COE, and proof of financial ability to cover living expenses in Japan.
Residence Card
Upon arrival in Japan, students are issued a residence card, which serves as proof of their legal status. The residence card must be carried at all times and may be required for various administrative procedures, such as opening a bank account or registering for national health insurance.
Learn more about the Japanese visa process on Wikipedia.
Cultural Adaptation and Integration
Adapting to a new culture and integrating into the local community is an important aspect of studying abroad. Here are some considerations:
Culture Shock
Adjusting to a new cultural environment may involve experiencing culture shock initially. This includes navigating different social norms, communication styles, and daily routines. However, universities often provide orientation programs and support services to help students navigate these challenges.
Language Learning
Learning the local language, whether Mandarin in China or Japanese in Japan, can facilitate cultural integration and enhance communication with locals. Language courses and language exchange programs at universities are valuable resources for language learning.
Engaging in Cultural Activities
Participating in cultural activities, such as joining clubs, attending local festivals, and exploring cultural heritage sites, provides opportunities to immerse oneself in the local culture. Building friendships with local students and actively engaging in community activities can enhance cultural understanding and integration.
Support Services
Universities in both China and Japan offer support services specifically designed for international students. These services may include academic assistance, counseling, cultural events, and mentorship programs, which contribute to a smooth transition and integration into the host country.
Career Opportunities and Networking
Job Market in China
China’s dynamic economy offers diverse job opportunities for both domestic and international graduates. Here are some key points about the job market:

Growing Industries
China’s job market is expanding in industries such as technology, finance, healthcare, renewable energy, e-commerce, and manufacturing. These sectors offer a range of career prospects and opportunities for professional growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the decision to study in China or Japan depends on individual preferences, academic goals, career aspirations, and personal circumstances. Both countries offer unique educational experiences, cultural immersion, and opportunities for personal and professional growth.
China’s educational system provides a wide range of academic programs, research opportunities, and affordability. With its rich cultural diversity and global economic influence, studying in China can offer unique insights and connections to one of the world’s fastest-growing economies.
Japan, on the other hand, is renowned for its academic excellence, technological advancements, and cultural heritage. Its universities are globally recognized, and studying in Japan can provide access to cutting-edge research, a unique cultural experience, and opportunities to be part of a global hub for innovation and technology.
Ultimately, it is essential to consider factors such as the educational system, program offerings, language requirements, living expenses, career prospects, and cultural fit when making a decision between studying in China or Japan. Conducting thorough research, seeking advice from professionals, and considering personal preferences will help prospective students make an informed choice.
Additional Resources
Useful Websites
Here are some useful websites for further information on studying in China or Japan:
- China Scholarship Council
- Study in China Guide
- Japan Student Services Organization (JASSO)
- Study in Japan Guide
Books and Publications
- “The International Student’s Guide to Studying in China” by Ming Yue and Wendy Zou
- “Studying in China: A Practical Handbook for Students” by Colin Speakman
- “The International Student’s Guide to Studying in Japan” by Gregory Hadley
- “Studying in Japan: A Handbook for International Students” by David J. Lu

