Yes, anyone can go to college in China, provided they meet the eligibility requirements. Chinese students typically must pass the Gaokao exam, while international students need proof of prior education, language proficiency, and a student visa.
Table of Contents
Eligibility for Attending College in China
Minimum Requirements for Chinese Students
All Chinese students who wish to attend college in China must first complete their nine-year compulsory education, which consists of six years of primary school and three years of junior secondary school. After completing their compulsory education, students are eligible to attend senior secondary school.
Senior secondary education is not compulsory but is highly sought after as it prepares students for the highly competitive National College Entrance Examination, or the Gaokao. Gaokao is a prerequisite for attending most universities in China.
Policies for International Students
International students seeking admission to Chinese universities typically must meet several requirements. These may include proof of completion of secondary education in their home country (equivalent to Chinese senior secondary education), proof of language proficiency (either in Chinese or English, depending on the language of instruction), and specific academic or entrance exam requirements depending on the institution.
International students also must obtain a student visa (X1 or X2) to study in China. This process typically involves submitting an application to the Chinese embassy or consulate in their home country, along with a letter of admission from the Chinese institution, proof of accommodation, and other necessary documentation.
Financial proof showing sufficient funds to cover tuition and living expenses during their stay in China is also typically required for international students. Some universities may also require health and medical insurance.
The Chinese Gaokao: A Gateway to Chinese Universities
Description of the Gaokao
The Gaokao, or the National Higher Education Entrance Examination, is a standardized exam administered annually in China. It is usually held over a period of two or three days in June, depending on the province.
The Gaokao covers a wide range of subjects, including Chinese, mathematics, and a foreign language (usually English), which are mandatory for all students. In addition, students must choose between two tracks: the humanities/social sciences track, which includes subjects like history, politics, and geography; or the science track, which includes physics, chemistry, and biology.
The Role of Gaokao in College Admission
The role of the Gaokao in college admissions in China is immense.
A student’s Gaokao score not only determines the university they can attend, but also the major they can study. Some universities and majors require higher scores than others.
Challenges of the Gaokao
There are numerous challenges associated with the Gaokao. One major challenge is the intense pressure and competition associated with the exam. This pressure can lead to severe stress and anxiety among students.
Another challenge of the Gaokao is its emphasis on rote memorization and lack of focus on critical thinking or creative skills. Critics argue that this structure doesn’t necessarily evaluate a student’s full academic potential or predict their success at university or beyond.
Wealthier families can afford resources like private tutoring or expensive test prep materials, giving their children an advantage. Additionally, urban students often have access to better educational resources than rural students, leading to a rural-urban education gap.
International Student Enrollment in Chinese Universities
Current Trends and Statistics
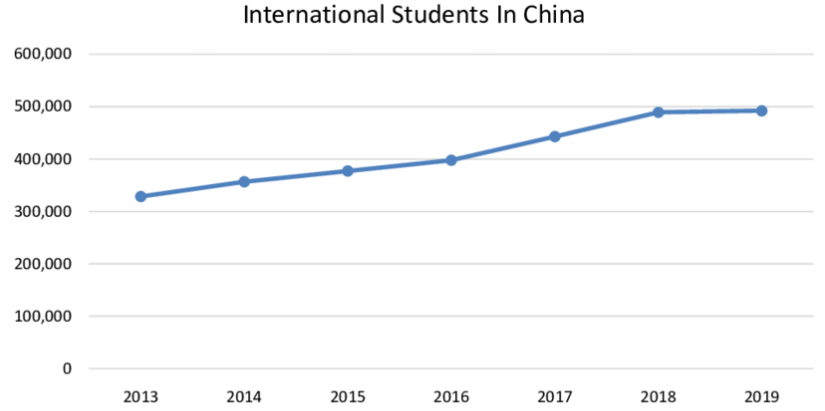
Over the past two decades, China has become an increasingly popular destination for international students. According to the Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China, the number of international students in China has grown significantly. The latest statistics show that China is now the third most popular destination for international students, behind the United States and the United Kingdom.
Students from Asia make up the largest proportion of international students in China, followed by those from Africa and Europe.
Application Process for International Students
The application process for international students varies from university to university. However, most universities require an online application, academic transcripts, a high school diploma or equivalent, language proficiency tests such as HSK (for courses taught in Chinese) or IELTS/TOEFL (for courses taught in English), and letters of recommendation.
After receiving a letter of acceptance from the university, international students must apply for a Chinese student visa (X1 for long-term study or X2 for short-term study). This usually involves a visit to the local Chinese embassy or consulate with the relevant documentation.
Scholarships and Financial Aid Opportunities
There are several scholarships and financial aid opportunities available for international students in China.
Many universities also offer their own scholarships. In addition, some provinces and cities offer local government scholarships. S
Financial aid is also available in some cases, often based on a student’s academic performance or financial need.
Alternative Paths to College Education in China
Vocational and Technical Colleges
Vocational and technical colleges provide an alternative route to university education in China, especially for students who wish to specialize in a specific trade or profession. These colleges offer courses in a variety of fields, including engineering technology, agriculture, medicine, economics, and business.
They typically offer three-year programs, culminating in a diploma.
Reference
- Education in China
- Higher education in China
- National College Entrance Examination
- Vocational education in China
- Distance education


